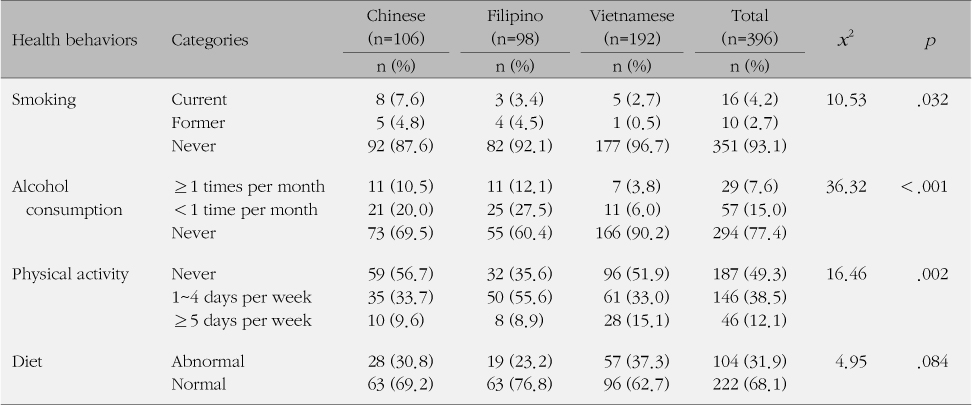
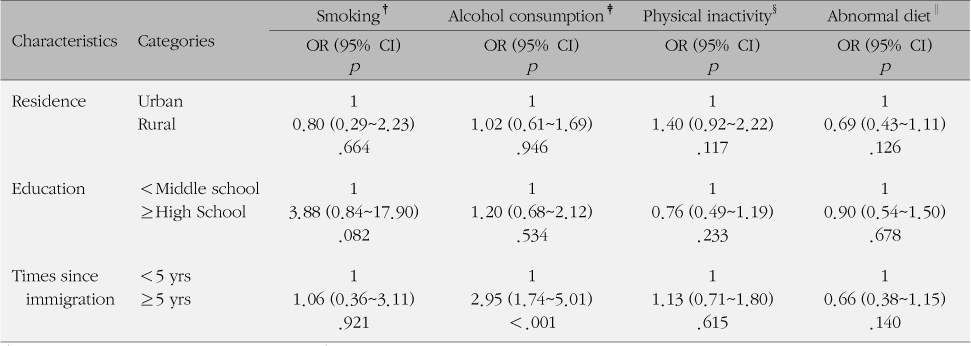
References
1. Ahn YH. Health status and health behavior of immigrant women married to Koreans. J Korean Acad Public Health Nurs 2008;22(1):18–25.
2. Allamani A, Innocenti FB, Innocenti A, Cipriani F, Voller F. Alcohol and tobacco consumption among Albanian immigrants in Florence. Subst Use Misuse 2009;44:282–300.
3. Balluz LS, Okoro CA, Nokdad A. Association between selected unhealthy lifestyle factors, body mass index, and chronic health conditions among individuals 50 years of age or older by race/ethnicity. Ethn Dis 2008;18(4):450–457.
4. Bolen JC, Rhodes L, Powell-Griner EE, Bland SD, Holtzman D. State-specific prevalence of selected health behaviors, by race and ethnicity: Behavioral risk factor surveillance system, 1997. MMWR CDC Surveill Summ 2000;49(2):1–60.
5. Chen J, Ng E, Wilkins R. The health of Canada's immigrants in 1994~1995. Health Rep 1996;7(4):33–45.
:37–50.
6. Dogra S, Meisner BA, Ardern CI. Variation in mode of physical activity by ethnicity and time since immigration: A cross-sectional analysis. Int J Behav Nutr Phys Act 2010;7:75.
7. Hyman I, Fenta H, Noh S. Gender and the smoking behaviour of Ethiopian immigrants in Toronto. Chronic Dis Can 2008;28(4):121–127.
8. Kim HR, Hwang NM, Jang IS, Yoon KJ, Kang BJ. Status and policy of reproductive health of marital immigrant women in Korea Seoul: Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs; 2008.
9. Kim MJ, Kim TI, Kwon YJ. A study on health promotion behavior and contraception in married immigrant women. Korean J Women Health Nurs 2008;14(4):323–332.
10. Kim ON. Mental health of immigrant women in rural communities: Focusing on acculturative stress and social support. Korean J Fam Welf 2007;12(3):47–73.
11. Kim SH, Kim WY, Lyu JE, Chung HW, Hwang RY. Dietary intakes and eating behaviors of Vietamese female immigrants to Korea through marriage and Korean spouses and correlations of their diets. Korean J Community Nutr 2009;14(1):22–30.
12. Kim SK, Kim YK, Cho AJ, Kim HR, Lee HK, Surl DH. Study on current status of multicultural families Seoul: Korea Ministry of Health & Welfare, Korea Ministry of Gender Equality & Family, Korea Ministry of Justice, & Korea Institute for Health and Social Affairs; 2010.
13. Kim WY, Cho MS, Lee HS. Development and validation of mini dietary assessment index for Koreans. Korean J Nutr 2003;36(1):83–92.
16. Korea Ministry of Health, Welfare and Family Affairs, & Korea Center for Disease Control and Prevention. 2007 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey statistics: The 4th Korea national health and nutrition examination survey Seoul: Author; 2009.
17. Lara M, Gamboa C, Kahramanian MI, Morales LS, Bautista DE. Acculturation and Latino health in the United States: A review of the literature and its sociopolitical context. Annu Rev Public Health 2005;26:367–397.
18. Lin LH, Hung CH. Vietnamese women immigrants' life adaptation, social support and depression. J Nurs Res 2007;15(4):243–254.
19. McDonald JT, Kennedy S. Insights into the 'healthy immigrant effect': Health status and health service use of immigrants to Canada. Soc Sci Med 2004;59(8):1613–1627.
20. Misra R, Patel TG, Davies D, Russo T. Health promotion behaviors of Gujurati Asian Indian immigrants in the United States. J Immigr Health 2000;2(4):223–230.
21. Mohan V. Why are Indians more prone to diabetes? J Assoc Physicians India 2004;52:468–474.
22. Newbold KB, Danforth J. Health status and Canada's immigrant population. Soc Sci Med 2003;57(10):1981–1995.
23. Nierkens V, de Vries H, Stronks K. Smoking in immigrants: Do socioeconomic gradients follow the pattern expected from the tobacco epidemic? Tob Control 2006;15:385–391.
25. Stephen E, Foote K, Hendershot G, Schoenborn C. Health of the foreign-born population. Adv Data 1994;241:1–12.