Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs > Volume 23(3); 2012 > Article
-
Original Article
- Correlates of Physical Activity among Korean Navy Personnel: An Ecological Approach
- Mi-Young Roh, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Chung-Yul Lee, Gwang-Suk Kim
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing 2012;23(3):296-306.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.0000/jkachn.2012.23.3.296
Published online: September 30, 2012
1Pohang Special Security Medical Cente, Pohang, Korea.
2College of Nursing, Nursing Policy Research Institute, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
Copyright © 2012 Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing
- 223 Views
- 0 Download
Abstract
-
Purpose
- This study was conducted to measure the relationships between ecological factors and Navy personnel's physical activity (PA) based on McLeroy's Ecological model.
-
Methods
- A cross-sectional survey was conducted with a convenience sample of 184 Navy personnel working in 10 Navyships. A self-reporting questionnaire consisted of measures of intrapersonal, interpersonal, organizational and community factors related to Navy personnel's PA. Data were analyzed by descriptive statistics, χ2-test, t-test, analysis of variance, and hierarchical multiple regression using SPSS/WIN 17.0 programs.
-
Results
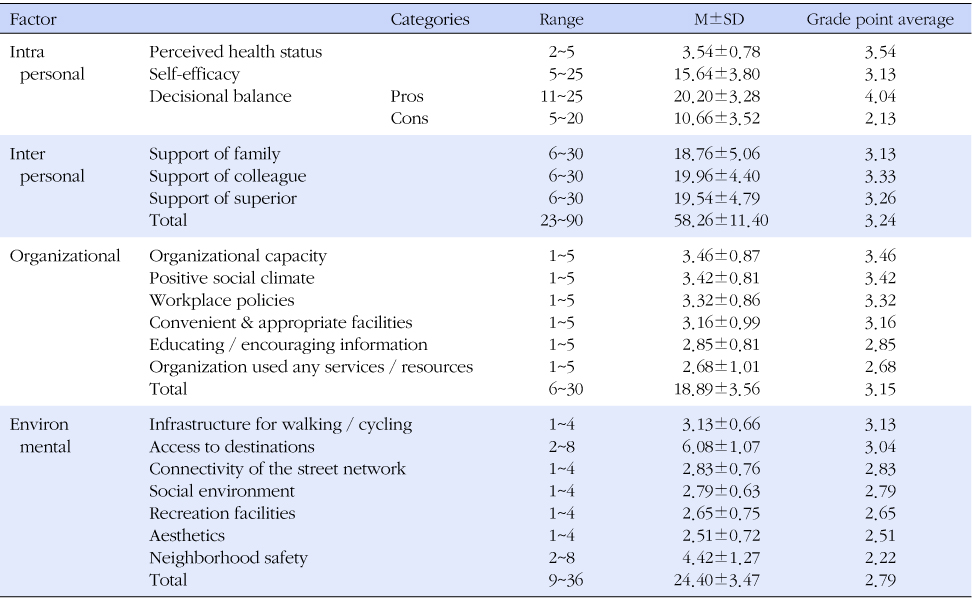
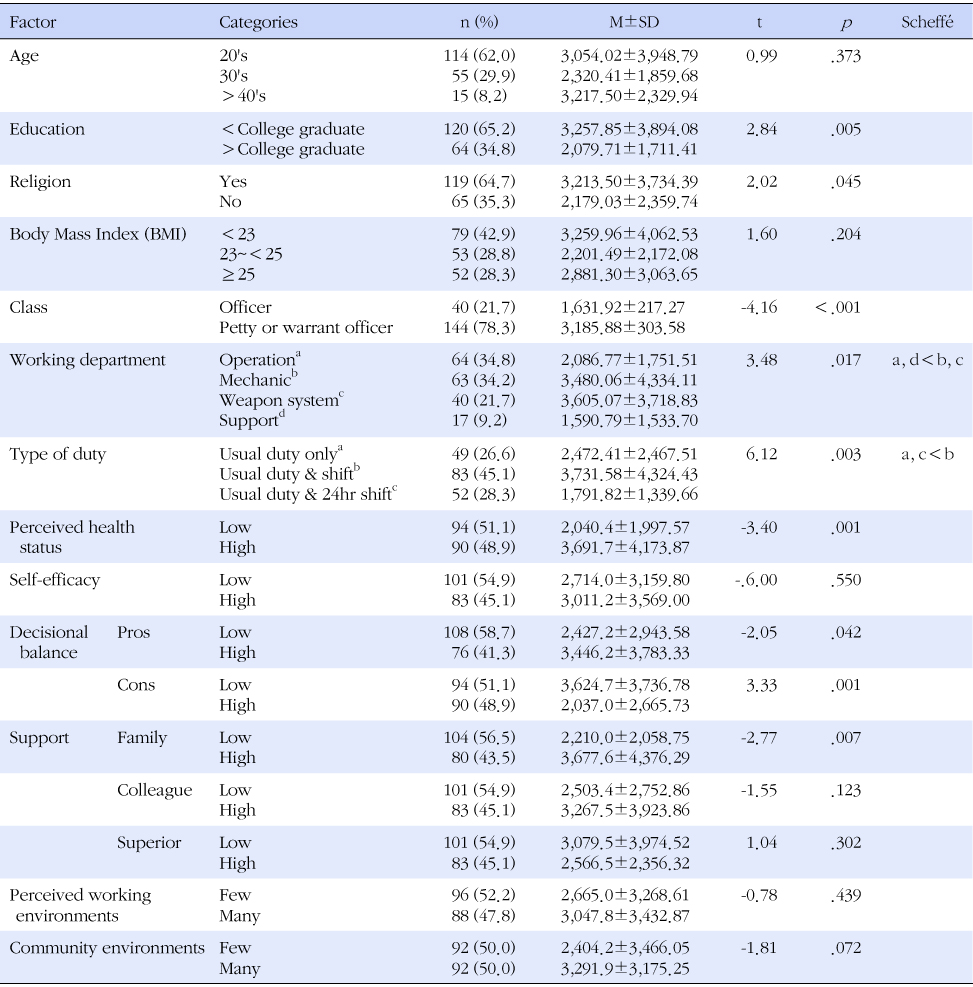
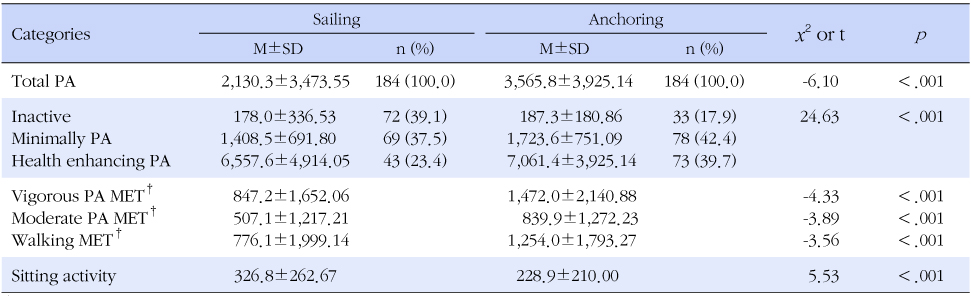
- Their mean PA level was 2,848.1±3,344.5 MET-min/week, and mostly moderate level (50.5%). Hierarchical multiple regression analysis showed that religion, working department, working type, perceived health status and community environment were significant PA correlates.
-
Conclusion
- Community environmental factors as well as intrapersonal factors were significantly associated with Navy personnel's PA, indicating that community health nurses should expand an approach for individual-level behavioral change to incorporate Navy personnel specific community environmental barriers into PA interventions.
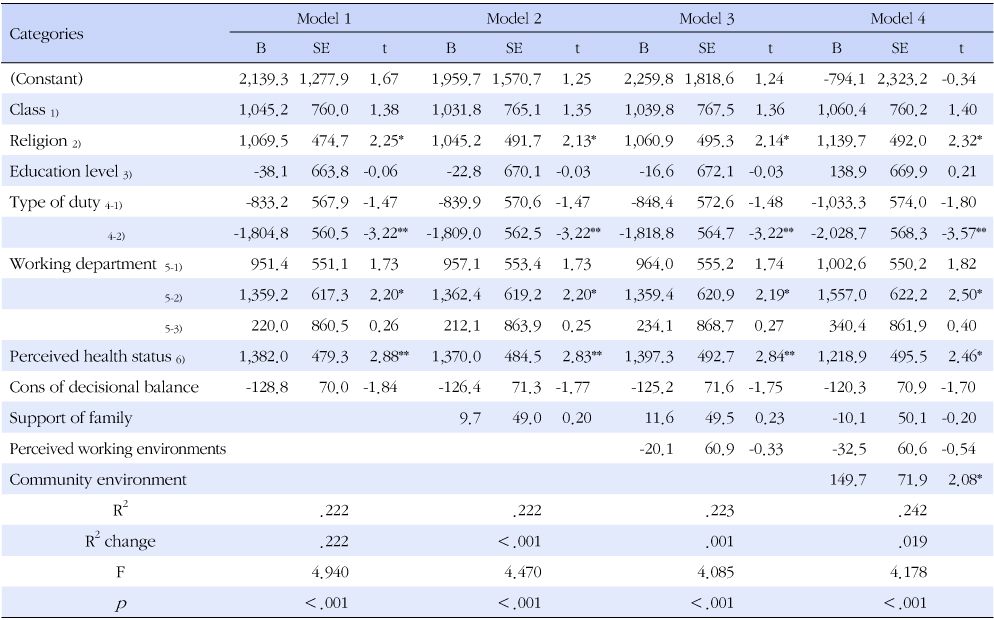
Dummy code: 1) officer 0, petty officer & warrent officer[WO] 1; 2) Do not have 0, Do have 1; 3) under graduate from college level 0, over graduate from college level 1; 4-1) usually duty 1, usually duty +3 shift 0, usually duty +24hr shift 0; 4-2) usually duty 0, usually duty +3 shift 0, usually duty +24hr shift 1; 5-1) operation part 0, mechanic part 1, weapon system part 0, support part 0; 5-2) operation part 0, mechanic part 0, weapon system part 1, support part 0; 5-3) operation part 0, mechanic part 0, weapon system part 0, support part 1; 6) under normal health 0, over healthy 1.
*p<.05, **p<.01.
- 1. Beresford SA, Bishop SK, Brunner NL, Duncan GE, McGregor BA, McLerran DF, et al. Environmental assessment at worksites after a multilevel intervention to promote activity and changes in eating: The PACE project. Journal of occupational and environmental medicine 2010;52:Suppl 1. S22–S28.
- 2. Bohnker BK. Analysis of navy physical evaluation board diagnosis. Military Medicine 2003;168(6):482.
- 3. Center for Disease Control and Prevention. Workplace health promotion 2010;Retrieved April 25, 2011. from http://www.cdc.gov/workplacehealthpromotion/implementation/topics/physical-activity.html
- 4. Choi JA. Construction of leisure physical activity model in middle-aged women 2005;Seoul: Seoul University; Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 5. Cho JH, Kang BM. Determinants of physical activity in environmental and social factor: A review. Korean Society for Measurement and Evaluation in Physical Education and Sports Science 2009;11(3):87–104.
- 6. Craig CL, Marshall AL, Sjostrom M, Bauman AE, Booth ML, Ainsworth BE, et al. International physical activity questionnaire: 12-country reliability and validity. Medicine & Science in Sports & Exercise 2003;35(8):1381–1395.
- 7. De Bourdeaudhuij I, Sallis JF, Saelens BE. Environmental correlates of physical activity in a sample of Belgian adults. American Journal of Health Promotion 2003;18(1):83–92.
- 8. Gauvin L, Levesque L, Richard L. Singer RN, Hausenblas HA, Janelle CM. Helping people initiate and maintain a more ctive lifestyle: A public health framework for physical activity promotion research. In: Handbook of Sport Psychology 2001;New York: John Wiley & Sons; 718–739.
- 9. Han KH, Song JE. Health and family-work role characteristics of middle aged men in Korea. Family and Culture 2001;13(1):51–73.
- 10. International Physical Activity Questionnaire Core Group. Guidelines for data processing and analysis of the International Physical Activity Questionnaire (IPAQ): Short and long forms 2005;Retrieved December 28, 2011. from http://www.ipaq.ki.se/scoring.pdf
- 11. Jun SH, Jeong ES, Ha HD, Kim JG, Lee SH. Research on the sick and wounded of seafarers and medical support system 2006;In: Paper presented at the meeting of the Korean Institute of Navigation and Port Research Conference; Seoul, Korea.
- 12. Ku HJ, Lee DT. Estimation of physical activity levels using International Physical Activity Questionnaires (IPAQ) in Korean college students. Journal of Sports Science Research 2006;24:65–73.
- 13. Lim DS. A study on the health concept, health promotion and practices behaviors of some soldiers: Focused of nurse officers 2005;Seoul: Kyung Hee University; Unpublished master's thesis.
- 14. Marcus BH, Selby VC, Niaura RS, Rossi JS. Self-efficacy and the stages of exercise behavior change. Research Quarterly for Exercise and Sport 1992;63:60–66.
- 15. McEachan BR, Lawton RJ, Jackson C, Conner M, Meads D, West R. Testing a workplace physical activity intervention: A cluster randomized controlled trial. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2011;8(29):1–12.
- 16. McLeroy KR, Bibeau D, Steckler A, Glanz K. An ecological perspective on health promotion programs. Health Education Quarterly 1988;15(4):351–377.
- 17. Ministry of Health and Welfare. Health plan 2020 2011;Seoul: Author.
- 18. Ministry of National Defense & Catholic University. Health promotion system and model development of the military 2009;Seoul: Author.
- 19. Mota J, Almeida M, Santos P, Ribeiro JC. Perceived neighborhood environments and physical activity in adolescents. Preventive Medicine 2005;41:834–836.
- 20. Nigg CR, Rossi JS, Norman GJ, Benisovich SV. Structure of decisional balance for exercise adaptation. Annals of Behavioral Medicines 1998;20:S211.
- 21. Oh JY, Yang YJ, Kim BS, Kang JH. Validity and reliability of Korean version of International Physical Activity Questionnaire short form. Journal of Korean Academy of Family Medicine 2007;28(7):532–541.
- 22. Prodaniuk TR, Plotnikoff RC, Spence JC, Wilson PM. The influence of self-efficacy and outcome expectations on the relationship between perceived environment and physical activity in the workplace. International Journal of Behavioral Nutrition and Physical Activity 2004;1(1):7.
- 23. Saelens BE, Sallis JF, Black JB, Chen D. Neighborhood-based differences in physical activity: An environment scale evaluation. American Journal of Public Health 2003;93(9):1552–1558.
- 24. Sallis JF, Bowles HR, Bauman A, Ainsworth E, Bull FC, Craig CL, et al. Neighborhood environments and physical activity among adults in 11 countries. American Journal of Preventive Medicine 2009;36(6):484–490.
- 25. Sallis JF, Grossman RM, Pinski RB, Patterson TL, Nader PR. The development of scales to measure social support for diet and exercise behaviors. Preventive Medicine 1987;16:825–836.
- 26. Seo GS. The patterns and related factors of exercise behavior changes of workers 2006;Daejeon: Chungnam National University; Unpublished doctoral dissertation.
- 27. Seok YS. Fitness level is lower in young soldiers than in older soldiers. Medical Today 2007;10 28 Retrieved August 27, 2012. from http://www.mdtoday.co.kr/mdtoday/index.html?no=35064
- 28. Shanas E. The health of older people: A social survey 1962;Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- 29. United States Department of Health and Human Services. 2008 Physical activity guidelines for Americans 2008;Retrieved April 25, 2011. from http://www.health.gov/paguidelines/guidelines
- 30. Yoo HJ, Lee JS. The research regarding the effect where the long period sailing goes made to a physical strength and that alternative. Oceanic Research Collection of Treatises 2002;29:369–387.
Figure & Data
References
Citations


 KACHN
KACHN
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

