Articles
- Page Path
- HOME > J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs > Volume 24(4); 2013 > Article
-
Original Article
- Factors Influencing Medication Adherence in Patients with Hypertension: Based on the 2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey
- Eunhee Cho, Chung Yul Lee, Insook Kim, Taewha Lee, Gwang Suk Kim, Hyeonkyeong Lee, Jisook Ko, Kyongeun Lee
-
Journal of Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing 2013;24(4):419-426.
DOI: https://doi.org/10.12799/jkachn.2013.24.4.419
Published online: December 31, 2013
1College of Nursing, Yonsei University, Seoul, Korea.
2School of Nursing, University of Texas, Austin, USA.
• Received: August 20, 2013 • Accepted: December 17, 2013
© 2013 Korean Academy of Community Health Nursing
This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial License (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-nc/3.0/) which permits unrestricted non-commercial use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
- 1,005 Views
- 2 Download
- 8 Crossref
Abstract
-
Purpose
- The purpose of this study is to examine factors influencing medication adherence in patients with hypertension.
-
Methods
- This study carried out a secondary analysis of data from the 2008 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Stratified sampling was used to select a participant sample that was representative of patients with hypertension throughout the country. Using the SPSS/WIN 18.0 program, data were analyzed using descriptive statistics, χ2 test, t-test, and logistic regression.
-
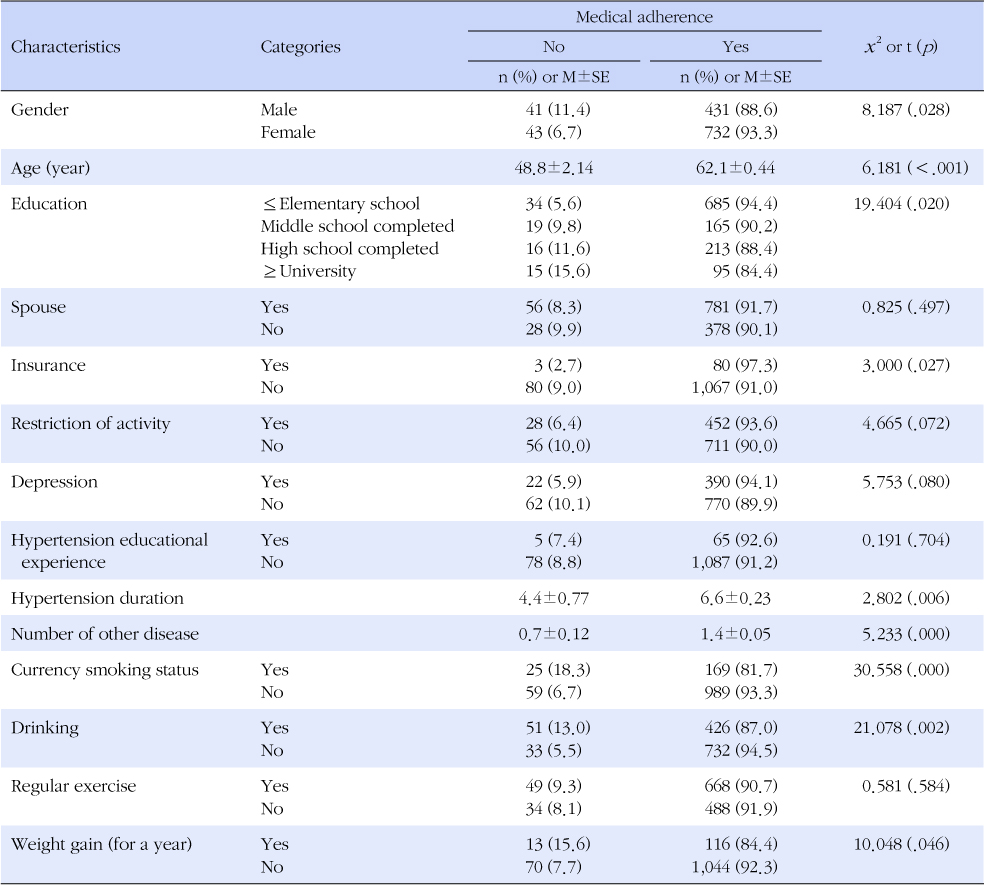
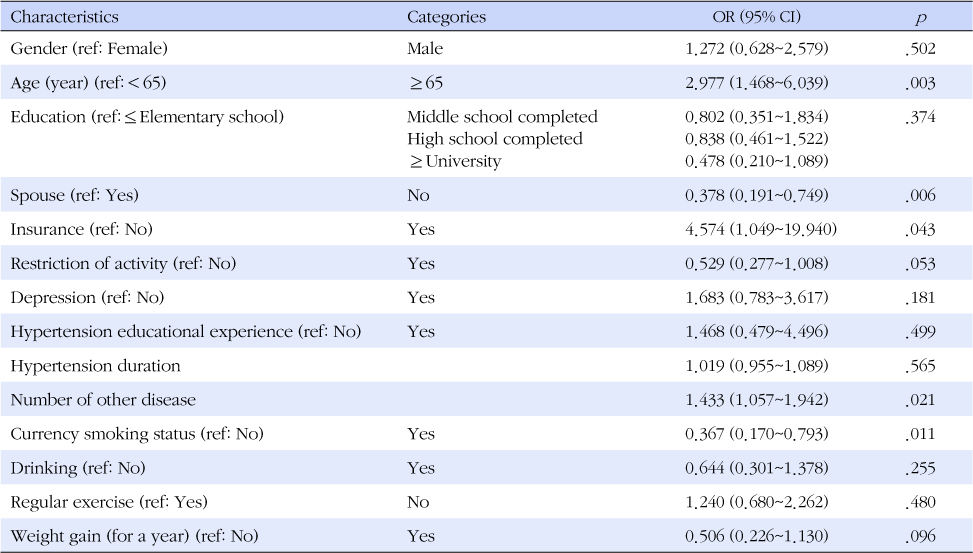
Results
- Of the patients with hypertension, 8.8% had showed non-adherence to medication. Medication adherence was associated with age, spouse, Medicare insurance, number of other diseases, and current smoking status. The cases with older age, a spouse, Medicare insurance, higher number of other diseases, and no current smoking status showed significantly high medication adherence.
-
Conclusion
- Nursing interventions and further studies are needed to achieve high levels of medication adherence based on factors influencing medication adherence such as age, spouse, Medicare insurance, number of other disease, and current smoking status.
Table 1General Characteristics, Health Status of Participants, and Health-related behaviors for Managing Hypertension (N=1,247)
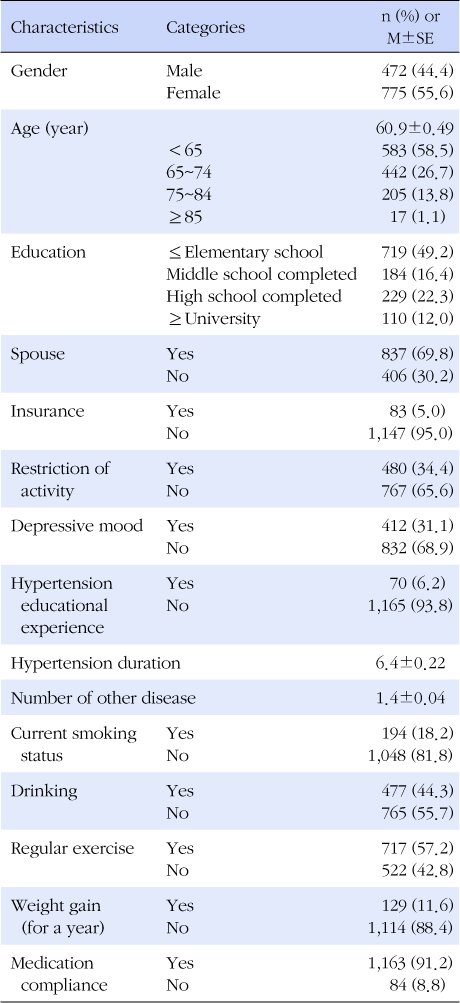

-
This study was supported by Department Research Program from the College of Nursing at Yonsei University.
NOTES
- 1. Barat I, Andersen F, Damsgaard EMS. Drug therapy in the elderly: What doctors believe and patients actually do. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 2001;51(6):615–622. ArticlePubMedPMCPDF
- 2. Beckman AG, Parker MG, Thorslund M. Can elderly people take their medicine? Patient Educ Couns. 2005;59(2):186–191. ArticlePubMed
- 3. Byeon YS, Kim SO, Cho JH. Factors influencing the stages of change in medication adherence in patients with hypertension. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2012;23(2):189–200. Article
- 4. Chang KO. The relationship among health habits, perceived health status and knowledge related to hypertension and medication compliances of hypertensive elderly. Busan: Catholic University; 2003. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 5. Chang YJ. Effects of a comprehensive education program on the self-efficacy and health behavior performance in patients with hypertension. Suwon: Ajou University; 2007. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 6. Choi SR. Prevalence and perception levels of essential hypertension -the third Korea national health and nutrition examination survey-. Seoul: Korea University; 2009. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 7. DiMatteo MR, Giordani PJ, Lepper HS, Croghan TW. Patient adherence and medical treatment outcomes: A meta-analysis. Med Care. 2002;40(9):794–811. PubMed
- 8. Han GS. Relationship of blood pressure control with healthy lifestyle practiceand medication adherence of hypertensive patients. Jeonju: Chonbuk National University; 2009. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 9. Kim JO. A study on management and health-related behaviors of the hypertensive patients. Busan: Inje University; 2011. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 10. Kim JS. The patterns of drug use in the elderly women with chronic disease in community. J Qual Res. 2006;7(1):67–76.
- 11. Kim JY, Lee DB, Cho YC, Lee SG, Chang SS, Kwon YH, et al. Study on health behavior of hypertensive patients and compliance for treatment of antihypertensive medicine. Korean J Rural Med. 2000;25(1):29–49.
- 12. Kim KE. A study on health behaviors and medication compliance of hypertensive patients in a rural area. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2002;13(1):49–56.
- 13. Kim SG, Kim SA, Park WS. Prevalence and management status of hypertension in Korea. J Korean Soc Hypertens. 2006;12(2):7–15.
- 14. Kim SO. The development and effects of a medication adherence intervention program for hypertensive patients. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2011;22(3):342–354. Article
- 15. Kim YJ. The effects of an education program on the knowledge of medication and prevention of depression in the elderly with chronic disease at a local community. J Korean Acad Community Health Nurs. 2011;22(4):399–408. Article
- 16. Lee JG. 2008 national health statistics report (3). Seoul: Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention; 2009.
- 17. Lee JK. Evaluation of a medication self-management education program for elders with hypertension living in the community. J Korean Acad Nurs. 2013;43(2):267–275. ArticlePubMed
- 18. Lee KA. The impact of medication adherence on healthcare utilization and expenditure. Seoul: Seoul National University; 2012. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 19. Lee YT. Working hours in Korea. The Korea Times 2011;Retrieved July 21, 2013. from http://news.hankooki.com/lpage/economy/201112/h2011123102311221500.htm
- 20. MacLaughlin EJ, Cynthia LR, Treadway AK, Sterling TL, Zoller DP, Bond CA. Assessing Medication Adherence in the elderly. Drug and Aging. 2005;22(3):231–255. ArticlePubMed
- 21. Min ES, Hur MH. Predictors of compliance in hypertensive patients. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2012;19(4):474–482. Article
- 22. Min SH, Kim JI. Construction of explanatory model for medication adherence in older people with chronic disease. J Korean Acad Fundam Nurs. 2012;19(4):463–473. Article
- 23. Ministry of Health Welfare. Community health survey. General Statistics (approval number. 11775) 2010;Retrieved July 12, 2013. from http://www.mw.go.kr/
- 24. Ministry of Health Welfare. 2012 community health survey 2013;Retrieved July 19, 2013. from http://www.mw.go.kr/front_new/al/sal0301vw.jsp?PAR_MENU_ID=04&MENU_ID=0403&CONT_SEQ=284380&page=1
- 25. Park JH, Shin YS, Lee SY, Lee SI. Antihypertensive drug medication adherence and its affecting factors in South Korea. Int J Cardiol. 2007;128(3):392–398. ArticlePubMed
- 26. Park SH. A study on drug abuse among the elderly. Daejeon: Hannam University; 2009. Unpublished master's thesis.
- 27. Sung J, Choi JH, On YK, Lee SC, Park SW, Gwon HC, et al. Study of compliance to antihypertensive medication in Korean hypertensive patients using medication event monitoring system. Korean Circ J. 2005;35(11):821–826. Article
- 28. Aronow WS. Treating hypertension in older adults. Drug Saf. 2009;32(2):111–118. ArticlePubMed
- 29. Willey C, Redding C, Stafford J, Garfield F, Geletko S, Flanigan T, et al. Stages of change for adherence with medication regimens of a measure. Clin Ther. 2000;22(7):858–871. PubMed
Figure & Data
References
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by 

- Factors Influencing the Control of Hypertension According to the Gender of Older Adults
Hye Young Choi, Eunha Kim
Healthcare.2023; 11(11): 1595. CrossRef - Association between Patient Experience and Medication Compliance of Dyslipidemia: Using Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (2015)
Ho-Hyoun Yim, Hwan-Sik Hwang, Hoon-Ki Park, Kye-Yeung Park, Miso Park
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2021; 42(2): 116. CrossRef - Medication Adherence and Effective Management of Hypertension
Seung-Won Oh
Korean Journal of Family Medicine.2021; 42(2): 89. CrossRef - Factors Influencing 1-Year Medication Adherence of Korean Ischemic Stroke Survivors
Gye-Gyoung Kim, Duck-Hee Chae, Man-Seok Park, Sung-Hee Yoo
International Journal of Behavioral Medicine.2020; 27(2): 225. CrossRef - Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of a Single-Pill Combination of Olmesartan/Amlodipine/Hydrochlorothiazide in Korean Patients with Essential Hypertension (RESOLVE): A Large, Observational, Retrospective, Cohort Study
Sung-Ji Park, Si Jae Rhee
Advances in Therapy.2020; 37(8): 3500. CrossRef - Factors Associated with Awareness, Treatment, and Control Rate of Hypertension among Korean Young Adults Aged 30–49 Years
Yong Woo Jeon, Hyeon Chang Kim
Korean Circulation Journal.2020; 50(12): 1077. CrossRef - Psychological Resistance to Drug Therapy in Patients with Hypertension: A Qualitative Thematic Analysis
Jiyeon Kang, Yeon Jin Jeong
Korean Journal of Adult Nursing.2020; 32(2): 124. CrossRef - Health Behaviors and Quality of Life in the Elderly with High Blood Pressure
So-Youn Bang, Sa-Sang Hyeon
Journal of Digital Contents Society.2018; 19(11): 2159. CrossRef
- We recommend
- Related articles
-
- Good subjective health status and health-related quality of life in people with chronic kidney disease: A secondary analysis using the Korea National Health and Nutritional Examination Survey in 2019 and 2020
- Prevalence and Risk Factors of Diabetic Retinopathy in Diabetes People using Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey VII

 KACHN
KACHN
 PubReader
PubReader Cite
Cite

